Aluminium Extraction Notes
Aluminium extraction
Extraction method:
Aluminium is a very reactive metal. It cannot be extracted using carbon because it is above carbon in the reactivity series ie. it is more reactive than carbon. So it is extracted through electrolysis.
Aluminium ore:
The aluminium ore is bauxite( impure aluminium oxide.)
The aluminium ore is bauxite( impure aluminium oxide.)
Major impurities in bauxite:
- The major impurities include Silicon dioxide, Iorn Oxide and Titanium dioxide.(SIT)
- Bauxite ore is heated in a pressure vessel along with a sodium hydroxide solution at a temperature of 150 to 200 °C.
- At these temperatures, the aluminium is dissolved to form sodium aluminate ( NaAlO2 )
- The insoluble impurities are removed by filtration.
- The sodium aluminate undergoes further treatment to form pure aluminium oxide.
Nature of the electrolyte:
The aluminium oxide must be melted so that electricity can pass through it.
The aluminium oxide must be melted so that electricity can pass through it.
Reducing the temperature of the electrolyte:
Pure aluminium oxide has a melting point of 2070°C Instead, molten cryolite (Na3AIF6) is used to reduce the temperature to and thus reduce energy costs.This reduces the melting point to 915°
Sometimes calcium fluoride is also added which further reduces the temperature further to 800°
Electrolytic Cell:
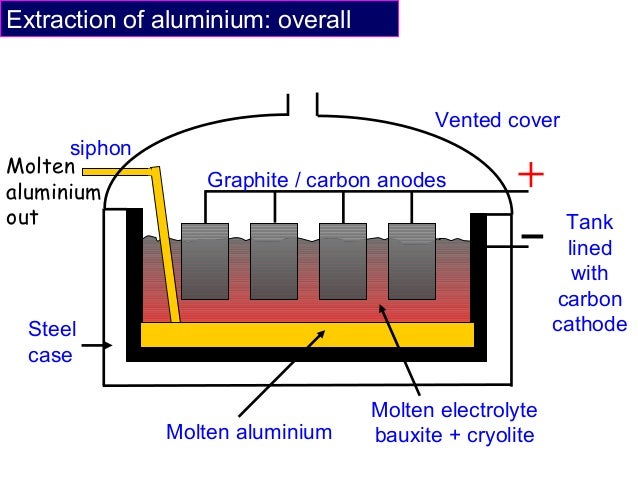
The steel container is coated with carbon (graphite) and this is the negative electrode (cathode).The anodes are also carbon electrodes
The reactions are as follows:
Al2O3(s) + 2 NaOH(aq) → 2 NaAlO2(aq) + H2O(l)
Sodium aluminate undergoes further treatment to form pure aluminium oxide.
Reactions at the electrodes:
At the cathode ( Reduction)
2Al3 (l)+ + 2O3+-(l) ---> 6Al(l) + 3O2(g)
Sodium aluminate undergoes further treatment to form pure aluminium oxide.
Reactions at the electrodes:
At the cathode ( Reduction)
Al3+ + 3e- ---> Al (s)
At the anode.( Oxidation)
At the anode.( Oxidation)
2O2- - 4e- ---> O2 (g)
- Aluminium metal forms at the cathode and sinks to the bottom of the tank, where it is tapped off.
- Oxygen forms at the anode. This oxygen reacts with the carbon of the anode , forming carbon dioxide, and they gradually burn away. Consequently, the anodes have to be replaced frequently.
The overall reaction is
2Al3 (l)+ + 2O3+-(l) ---> 6Al(l) + 3O2(g)
Gases given out:
Oxygen is discharged at the positive carbon (graphite) anode.Oxygen reacts with the carbon anode to form carbon dioxide gas.
Oxygen is discharged at the positive carbon (graphite) anode.Oxygen reacts with the carbon anode to form carbon dioxide gas.
carbon + oxygen carbon dioxide
C(s) + O2(g) CO2(g)
C(s) + O2(g) CO2(g)
Why carbon anode needs to be replaced?
The carbon anode slowly reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide and hence needs to be replaced regularly.
The carbon anode slowly reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide and hence needs to be replaced regularly.
Comments
Post a Comment